U.S. IRS Tax Revenue by Year from 1999 to 2023 | Cornerstone
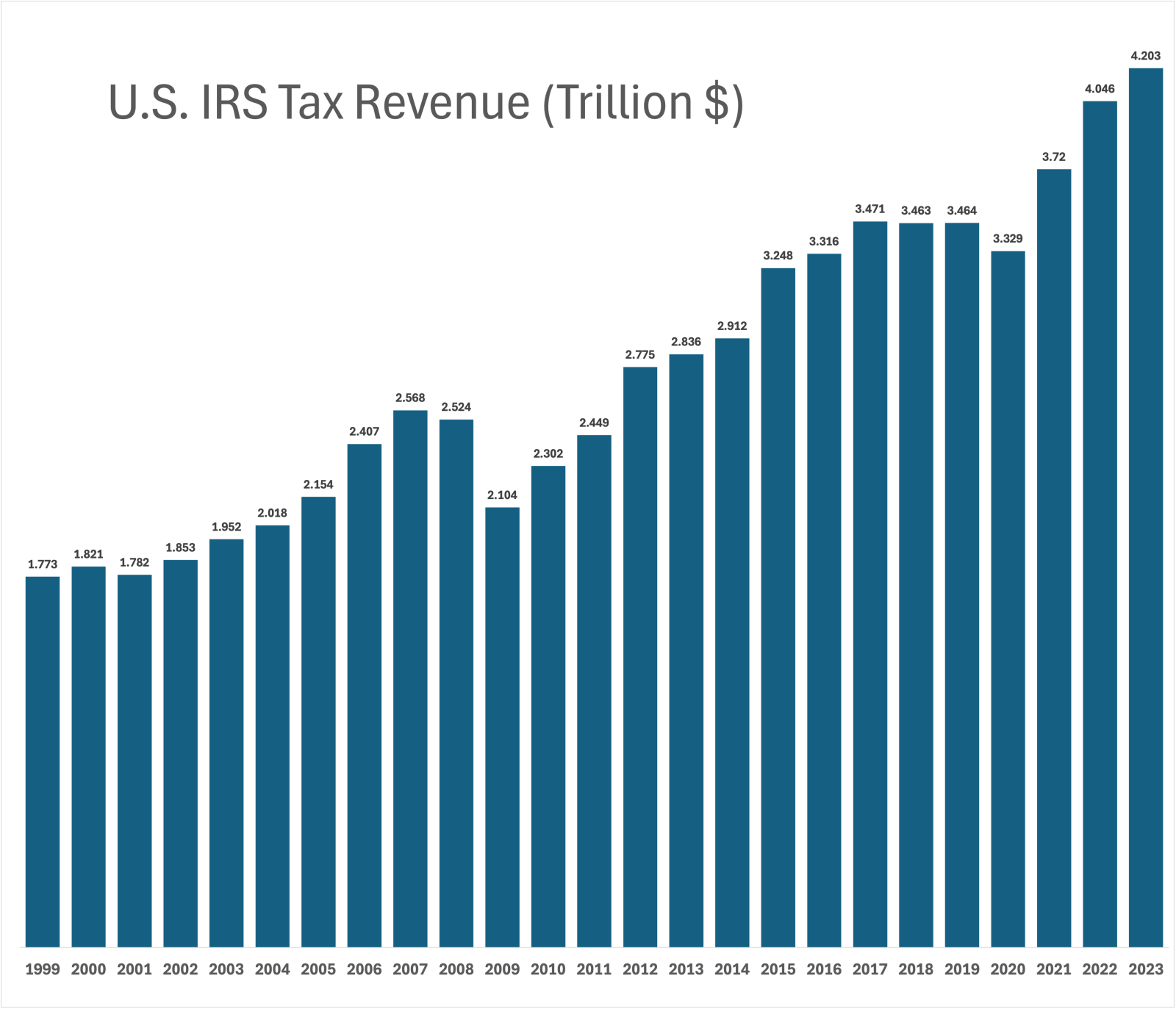
| Year | Tax Revenue (Trillion $) |
|---|---|
| 1999 | 1.773 |
| 2000 | 1.821 |
| 2001 | 1.782 |
| 2002 | 1.853 |
| 2003 | 1.952 |
| 2004 | 2.018 |
| 2005 | 2.154 |
| 2006 | 2.407 |
| 2007 | 2.568 |
| 2008 | 2.524 |
| 2009 | 2.104 |
| 2010 | 2.302 |
| 2011 | 2.449 |
| 2012 | 2.775 |
| 2013 | 2.836 |
| 2014 | 2.912 |
| 2015 | 3.248 |
| 2016 | 3.316 |
| 2017 | 3.471 |
| 2018 | 3.463 |
| 2019 | 3.464 |
| 2020 | 3.329 |
| 2021 | 3.720 |
| 2022 | 4.046 |
| 2023 | 4.203 |
IRS Tax Revenue Trends (1993-2022)
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has collected increasing amounts of tax revenue over the past three decades, with some fluctuations due to economic conditions and policy changes.
Key Observations
- Overall Trend: Tax revenue has generally increased over the 30-year period, reflecting economic growth and inflation.
- Recent Peak: In Fiscal Year 2022, the IRS collected more than $4.9 trillion in gross taxes.
- Major Revenue Sources: Individual income taxes, business income taxes, and employment taxes consistently form the bulk of IRS collections.
Revenue Breakdown for Fiscal Year 2022
- Total Gross Collections: Over $4.9 trillion
- Individual Income Taxes: More than $2.8 trillion (including withholding and payments)
- Business Income Taxes: Nearly $475.9 billion
- Employment Taxes: A significant portion, though exact figure not provided in the search results
- Estate, Gift, and Excise Taxes: Smaller but still substantial contributions
Historical Context
- 1990s: The economy experienced strong growth, leading to increased tax revenues.
- Early 2000s: Tax cuts and economic slowdown affected revenue growth.
- 2008-2009: The Great Recession caused a significant dip in tax collections.
- 2010s: Gradual recovery and economic expansion led to rising revenues.
- 2020-2022: The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent economic measures greatly impacted tax collections and distributions.
Recent Developments
- COVID-19 Impact: The IRS implemented various relief measures, including Economic Impact Payments totaling more than $815 billion and advance Child Tax Credit payments of $93 billion.
- Electronic Filing: In FY 2022, 93.8% of individual tax returns were filed electronically, improving efficiency.
- Refunds: The IRS issued almost 242.1 million refunds in FY 2022, amounting to more than $641.7 billion.