 PLUS: 6 major factors impacting bonuses. And 4 notes from a master.
PLUS: 6 major factors impacting bonuses. And 4 notes from a master.
By Marc Rosenberg
Partner Comp: Art & Science
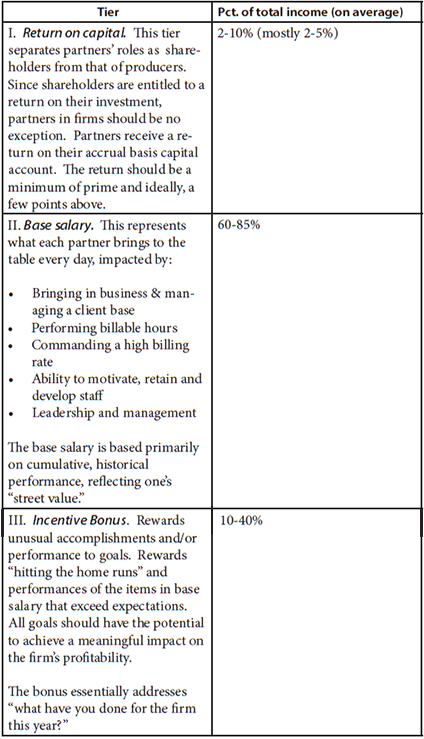
Most CPA firm partner compensation systems consist of three tiers, each of which compensates the partners in a different way.
MORE ON PARTNER COMPENSATION: Partner Compensation 101| What Partners Earn and How They Earn It | Partner Compensation: An Art, Not a Science | How Partners View Compensation: It’s Not All about the Money | Why Most Partner Comp Systems Are Performance-Based
What is base compensation (or salary)?
It’s common to define partners’ base compensation as their historical or street value to the firm. What they bring to the firm every day. A managing partner once told me: “It’s what we would have to pay a partner at another firm to come work with us.”
Practice debunked: Many firms have equal bases for all partners. Their thinking is that the base is merely a level of compensation that (1) is above what managers are paid and (2) is enough for the partners to live comfortably on. Firms like this are operating a modified pay-equal system, which is widely viewed in the CPA industry as ineffective and unfair. Not only do partners NOT perform equally, there is almost always a wide variation from highest to lowest performer. The case for equal bases is a weak one at best.
Practice debunked: I’ve seen some firms impute partner bases as follows: First, compute hourly pay rate by dividing the standard billing rate by the firm’s billing rate multiple. Then, multiply the hourly pay rate by 2,000 hours to arrive at imputed base pay. Billing rate multiple is a staff person’s billing rate divided by the hourly pay rate. Eighty to ninety percent of all firms are in the 3.5 to 4.0 range.
TO READ THE FULL ARTICLE
